JIANGSU KITECH MACHINERY CO.,LTD

| Source of High-Contamination PE Film | Description |
| Agricultural Films (e.g., mulch films) | Used for crop protection and soil moisture retention, often heavily contaminated with soil, pesticides, and fertilizers. |
| Packaging Waste (e.g., food wrappers) | Includes single-use packaging films contaminated with food remnants, oils, and organic matter. |
| Post-Consumer Films | Includes plastic bags, wraps, and films from household waste, often containing food residues, oils, and dirt. |
| Construction Films | Used for weather protection on construction sites, commonly contaminated with dirt and debris. |
| Contaminant Type | Impact on PE Film Washing Line |
| Soil and Sand | Clogs filtration systems and reduces the effectiveness of water circulation, increasing wear on pumps and filters. |
| Oil and Grease | These contaminants adhere strongly to the PE film, requiring additional steps like hot washing or the use of surfactants to break them down. |
| Organic Residues | Organic matter, such as food waste or plant residue, can block washing equipment, leading to inefficient cleaning and potential bacterial growth in the system. |
If the above contaminants are not properly removed, inefficiencies in PE film washing line result in extra maintenance and produce low quality recycled product. This will reduce efficiency of recycling process and raise operating cost.
Heavy soiling of PE films is causing some challenge to PE film washing lines. The most severe challenge areas where the operators are facing the challenge are:
·Choking of Filtration System: Filtration systems will clog immediately when high levels of soil and organic grime combine, inhibiting water flow and the possibility of damaging filtration and pumping equipment. This causes expensive cleaning and maintenance downtime.
·Ineffective Removal of Contaminants: Sticky residues and oils cannot be eliminated effectively by simply washing with plain cold water. They must undergo treatment with chemicals or heat, and the operation becomes more complex.
·Greater Energy and Water Usage: More forceful wash cycles and increased temperatures are required, which increases energy and water usage, and once again operational costs are driven up.
·Lower Quality of Recycled Material: Besides the elimination of impurities entirely, the recycled product of PE film also has a lower market value and quality.
These are some of the problems that necessitate the demand for more advanced technology and processes in washing high-contamination PE films more effectively. In the following sections, we will explain effective solutions, such as optimized equipment design and higher-level washing processes, that can address these problems.
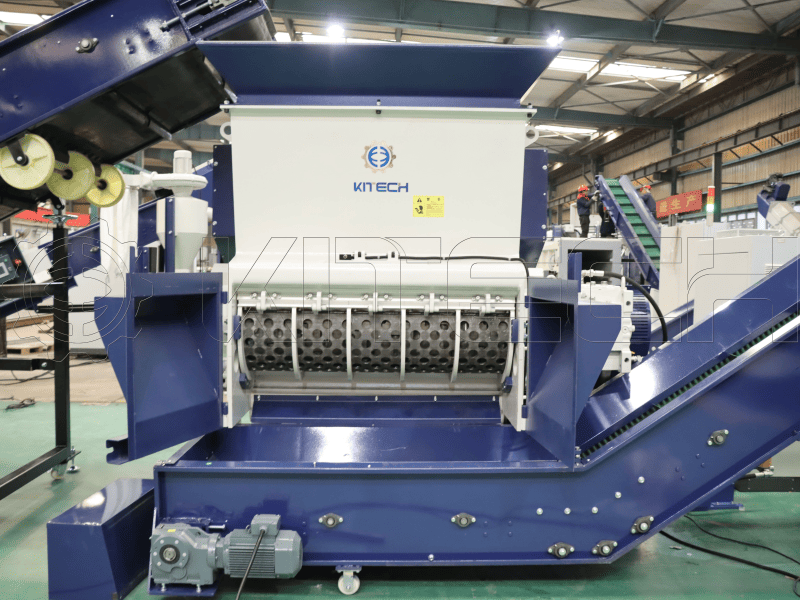

| Shredder Type | Function | Key Features |
| Heavy-Duty Shredder | Reduces large, contaminated PE films into smaller pieces for easier washing | High torque motor, durable blades, variable speed |
| Dual Shaft Shredder | Provides high throughput and can handle larger contamination loads | More efficient for films with mixed contaminants like soil and plastic |
| Washer Type | Function | Key Features |
| Single-Paddle Washer | Scrubs away dirt and oils with minimal water usage | Cost-effective, suitable for medium contamination levels |
| Double-Paddle Washer | Provides more intense scrubbing action for films with higher contamination levels | Enhanced cleaning efficiency with increased agitation |
| Hot Washing System | Function | Key Features |
| Hot Water Wash | Uses heated water to dissolve and remove oils and grease | Temperature-controlled, energy-efficient |
| Chemical Hot Wash | Adds surfactants or alkaline chemicals to enhance cleaning power | Suitable for stubborn grease and organic residue removal |
| Rinsing Tank Type | Function | Key Features |
| Single-Stage Rinsing | Basic rinsing to remove residual chemicals and particles | Low cost, effective for lighter contamination |
| Multi-Stage Rinsing | Multiple rinsing stages for thorough cleaning of heavily contaminated films | Ensures full removal of contaminants, suitable for high-pollution PE films |
| Filtration System | Function | Key Features |
| Coarse Filtration | Removes large particles and debris from the water before reuse | Easy to maintain, ensures effective water flow |
| Fine Filtration | Filters smaller particles such as oils, dirt, and organic residues | High-efficiency filtration for cleaner water |
| Membrane Filtration | Provides fine filtration for water with high levels of contaminants | Suitable for greasy or highly polluted water |

| Temperature Range | Application Target | Effectiveness |
| 60–70°C | Light grease, food residue | Moderate |
| 70–80°C | Industrial oils, adhesives | High |
| 80–90°C | Heavy grease, multilayer films | Very High |
Introducing specific cleaning agents into the washing process further improves the line’s ability to remove complex contaminants.
| Chemical Additive | Function | Recommended Dosage* |
| Caustic Soda (NaOH) | Breaks down grease and organic matter | 0.3–1.0% solution |
| Surfactants | Reduces surface tension for better penetration | 0.05–0.2% |
| Defoamers | Controls foam formation in washing tanks | As needed |
| Oxidizing Agents | Removes odor and organic stains (optional) | Case-dependent |
*Exact dosage depends on contamination level, tank size, and water hardness.
Though chemicals and hot washing maximize return on cleaning, they maximize operating expenses and environmental impacts. To maximize ideal best balance:
·Re-circulation reused hot re-circulated water wherever feasible with closed-loop circulation.
·Control chemical concentration proportionally and evenly in film charging.
·Install high-efficiency heaters or solar thermal pre-heating as an eco-friendly alternative.
High-contamination PE film processing is generally energy-intensive, especially in warm washing, drying, and mechanical cutting. In addition to this, the huge amount of wastewater generated through washing can cause increased disposal cost and environmental footprint.
| Process Stage | Energy Consumption (%) | Water Usage (ton per hour) | Main Challenges |
| Shredding & Crushing | 15–20% | 0–3 | High mechanical energy demand |
| Hot Washing | 5–10% | 0.5–1 | Energy-intensive heating |
| Friction Washing | 10–15% | 9–10 | Requires strong water flow to ensure cleanliness |
| Floating washing | 3–5% | 1–2 | Large water use |
| Squeezing dryer | 15–20% | 0 | High mechanical energy demand |
| Water Filtration & Recycling | 5–10% | 15–20 | Heavy demand on filtration and recirculation systems |
4.2 Water Recycling and Filtration Systems
A closed recycling loop system is a must in attempting to manage the huge volume of wastewater resulting from washing. Efficient filtration enables water recycling and reduces waste and operating expense.
| Water Treatment Module | Function | Efficiency Considerations |
| Sedimentation Tank | Settles heavier solids before filtration | Reduces filter clogging |
| Coarse Filtration | Removes large particles and debris | Should be checked regularly for blockages |
| Fine Filtration | Filters out finer particles using mesh or screen filters | Efficiency varies with particle size |
| Membrane Filtration (optional) | High-efficiency filtration for fine particulates like oils and inks | Reduces water waste; more costly |
Efficient energy management reduces costs and environmental impact. Several strategies can be employed to optimize energy usage across the washing line.
| Strategy | Description | Potential Savings (%) |
| Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) | Adjusts motor speed to match load requirements in shredders and washers | 10–15% reduction in energy consumption |
| Heat Recovery Systems | Captures waste heat from hot washing and drying to preheat water | 20–30% reduction in heating energy |
| Energy-Efficient Motors | Upgrades to high-efficiency motors in all major equipment | 5–10% reduction in total energy consumption |
| Smart Control Systems | Uses sensors and AI to optimize process parameters based on real-time data | 10–20% reduction in energy and water use |
| Solar Thermal Pre-Heating | Uses solar energy to preheat wash water before entering the system | Can reduce 15–25% of energy costs annually |
·Film Pre-Treatment: Use a coarse screen before washing to remove large trash, saving water and filter system capacity.
·Extra Washing Time and Temperature: Decrease wash cycle length and raise temperature control for fewer energy units used when washing hot.
·High-Efficiency Drying Technology: High-technology drying equipment, i.e., low-energy centrifugal dryers should be implemented to minimize energy consumed in drying processes.
·Wastewater Neutralization: Monitor and neutralize wastewater pH on a regular basis to avoid clogging of the system and increase recycling efficiency.
By implementing all of these measures in a PE film washing line, recycling plants can realize significant water and energy savings combined with acceptable cleaning performance and sustainability.
Maintaining high operational efficiency requires constant attention to several aspects of the washing process, from pre-treatment to final drying.
| Operational Aspect | Key Considerations |
| Pre-Treatment (Screening) | Properly screen films before washing to remove large debris and contaminants, reducing the load on washing and filtration systems |
| Water Temperature Control | Ensure consistent water temperature during hot washing to optimize cleaning and reduce energy consumption |
| Cycle Time Management | Fine-tune washing and drying times to avoid overuse of water and energy, preventing unnecessary wear |
| Contamination Type Handling | Adjust the washing process based on the type of contamination (e.g., grease, soil, organic matter) to improve cleaning efficiency |
| Maintenance of Water Quality | Regularly monitor water quality, especially pH levels and turbidity, to ensure effective filtration and reuse in the system |
To prevent unexpected downtime and maintain high processing standards, a comprehensive maintenance schedule must be followed.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Purpose |
| Filter and Screen Replacement | Every 3–6 months | Ensure filtration components (coarse and fine filters) are free from clogs to maintain water flow and system efficiency |
| Lubrication of Moving Parts | Every 3 months | Lubricate shredder blades, agitators, and friction washers to minimize wear and reduce operational friction |
| Inspection of Heating Units | Every 6 months | Check for scaling, damaged heating elements, or inefficient heat exchangers that could reduce thermal efficiency |
| Check for Wear and Tear on Shredders | Quarterly | Inspect blades and motors for signs of damage and replace as necessary to ensure smooth shredding of heavily contaminated film |
| Cleaning of Water Recirculation System | Every 2 months | Remove sediment buildup in the recirculation system to prevent clogging and ensure efficient filtration and recycling of water |
Certain components of the washing line are particularly susceptible to wear when dealing with high contamination loads. Focused attention on these parts is vital for maintaining efficiency.
| Component | Maintenance Focus | Action Plan |
| Shredder Blades | Prone to dulling due to abrasive contaminants like dirt and stones | Regular sharpening or replacement to avoid breakdowns |
| Friction Washer Paddles | Wear from constant agitation of dirty film | Check for cracks or warping; replace paddles when necessary |
| Water Filtration System | Clogs due to fine particulates (dirt, grease) | Clean filters regularly; replace membranes as needed |
| Drying Equipment | Overheating or inadequate moisture removal | Ensure proper calibration of drying temperatures and monitor energy consumption |
Foreign objects (e.g., metal pieces, large plastics) can accumulate in the system, potentially causing equipment damage or inefficiency.
| Source of Foreign Objects | Prevention Method |
| Contaminated Film | Use magnetic and non-metallic debris separators before shredding |
| Packaging Materials | Install label removers to prevent label buildup during washing |
| Field-Contaminated Films | Integrate pre-scraping systems to remove soil, sand, and rocks |
There should be regular checks in order to ensure that all that is in the system is in its best state of operational effectiveness. Problems will be detected before they lead to widespread breakdowns with regular scheduled inspection.
| Inspection Focus | Key Points to Check |
| Electrical and Mechanical Systems | Monitor for unusual vibrations, motor overheating, or inconsistent speed |
| Water Flow and Recirculation | Check pumps, valves, and pressure gauges for leaks or clogs |
| Heat Exchangers and Boilers | Inspect for corrosion or build-up of mineral deposits that reduce efficiency |
| Seals and Gaskets | Regularly check for wear or damage to avoid leaks and water loss |
By applying these work instructions and instructing the plant to normal operating conditions, recycling plants are able to successfully and effectively run their PE film washing lines even under a high percentage of dirty material.
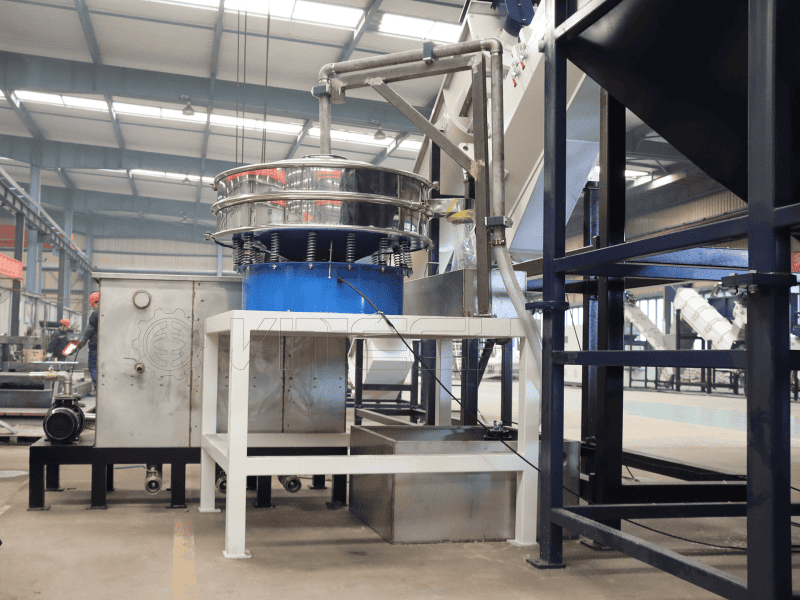

Efficient recycling of heavily contaminated PE film waste is more than mere washing processes in the general sense—it is a task involving well-designed, multi-stage PE film washing line for heavy contaminations cleaning. Irrespective of pre-treatment and mechanical washing, or thermal and chemical washing, all processes are necessary to making the final product clean, and also recyclable.
By using the most advanced washing technology, reducing energy and water usage, and employing strict operating regimes, recyclers can achieve maximum quality output and reduce operating and environmental costs. With growing pressure on high-quality recycled products, it's not only in their interest—it's the way to stay competitive and viable in the world recycling economy—to invest in the proper washing line technologies for soiled film waste.